Can I weld ASTM A387 Gr22 and 304 steel plate together?
The welding of dissimilar steel has a wide application in the field such as aerospace, petrochemical industry, machinery industry. The dissimilar steel is really different in chemical composition, metallurgical compatibility and physical properties and etc., which will appear of alloy element migration, uneven chemical composition and metallographic organizations in the welding process, also can produce thermal stress and welding deformation or cracks, this will reduce the mechanical properties of welded joints. In this paper, the weldability of dissimilar steel welded joints of ASTM A387 GR22 Chromoly steel plate and S30408 stainless steel plate was analyzed, and the appropriate welding methods, welding materials and welding process parameters were selected, as well as the post-welding heat treatment.
| Grades | C | Si | Mn | Cr | Mo | Cu | Ni | N | P | S |
| A387 GR22 | 0.11 | 0.35 | 0.46 | 2.21 | 1.06 | 0.12 | 0.22 | / | 0.01 | 0.006 |
| 304 | 0.05 | 0.62 | 1.83 | 19.16 | / | / | 8.97 | 0.06 | 0.027 | 0.015 |
S30408 is a commonly used Austenitic stainless steel, ASTM A387 GR22 is a low alloy heat resistant steel with good high-temperature resistance and resistance to hydrogen, mainly used in hydrogenation plant reactor and heat exchanger and other equipment. Chromium and molybdenum can significantly improve the hardenability of steel, and , the weld metal and heat-affected zone may form microstructure sensitive to cold cracking at a specific cooling rate. Progressive embrittlement occurs when the total content of hazardous residual metals exceeds the allowable limit at 350-550℃ for long periods of operation. The main difficulties we have to face are:
- Dilution of weld
The weld metal is diluted by the deposited metal during the welding process. A transition layer is formed in the weld metal close to the fusion zone on one side of the ASTM A387 GR22 steel plate. The composition of the transition layer is different from that of the weld metal. The higher the base metal alloy content is, the higher the fusion ratio is and the higher the dilution rate is. The transition layer on the ASTM A387 GR22 side may produce a brittle Martensite structure due to dilution.
- Carbon migration
Chromium and carbon atoms under high temperature is easy to form compounds of chromium carbide, ASTM A387 Gr22 steel plate side forms carbon atoms from decarburization area due to poor chromium in the process of welding, in turn, softening, coarse grains, increase brittleness, corrosion resistance, and S30408 side for enriching chromium and carbon atoms to form the carburization layer migration, and hardening, grain size and performance better.
- Welding stress
Due to the different thermal conductivity and linear expansion coefficient of the two materials, thermal stress will be generated in the high temperature zone during the welding process, which cannot be eliminated, resulting in additional stress near the weld and fusion zone, and welding residual stress generated in the cooling process due to inconsistent shrinkage, resulting in cracks on the side of ASTM A387GR22 steel plate.
After knowing the possible problems, the materials for this experiment are ASTM A387GR22 and S30408 stainless steel plates, with specifications of 400mm×150mm×10mm. The chemical composition of the two materials is shown in the table:
- Welding method
In order to reduce the dilution of welding joints and prevent cold crack and reheat crack, nickel-based alloy welding material is first surfaced on the side of ASTM A387GR22 during welding. Welding methods with small fusion ratio and low dilution rate are selected, such as argon tungsten arc welding and electrode arc welding. In this experiment, the argon arc welding is used as the backing and the welding method of arc welding cover.
- Welding Materials
Nickel-based electrodes and wires ERNiCr-3/ENiCr-3 are used to block the formation of carbide by the graphitization of nickel, reduce the transition layer and prevent the generation of brittle martensite structure, and further inhibit the carbon migration in ASTM A387GR22 steel plate.
- Welding groove
The type of welding groove should consider the number of welding layers, the amount of filling metal and the fusion ratio and the welding residual stress. The type and size of the designed groove are shown below:
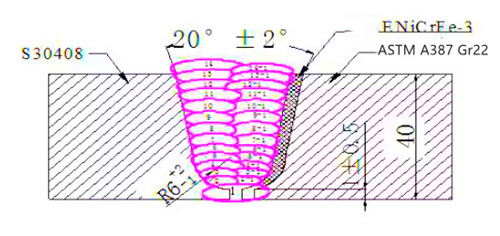
- Preheating and interlayer temperature control
The microstructure of ASTM A387 GR22 is tempered bainite and that of S30408 is Austenite. The former has hardenability, reheat crack tendency and tempering brittleness, while the latter has good weldability. According to the chemical composition, joint form, welding method and welding material of the materials, we determined that the preheating temperature was about 200℃, and the temperature between the welding passes was within 100℃. After welding, the heat treatment was conducted at 350℃×2h immediately.
- Welding process parameter
| Welding layer | Welding Methods | Welding wires | Welding electrode | Welding current I/A | Welding pressure U/V | Welding speed v/cm |
| Surfacing | SMAW | ERNiCr-3, 4.0mm | DCEP | 140-160 | 23-26 | 16-20 |
| Spot welding/1 | GTAW | ERNiCr-3, 2.4mm | DCSP | 120-150 | 13-15 | 8-10 |
| 2-end | SMAW | ERNiCr-3, 4.0mm | DCEP | 140-160 | 23-26 | 16-20 |
Before welding, clean up the oxide layer, oil, moisture, rust, etc. within 200mm of the groove and both sides of the steel plate. The specific welding process parameters are shown in the table.
- Post-weld stress relief heat treatment
Post-welding stress relief heat treatment is an important process to prevent welding cracks. Large welding residual stress will be generated during welding, so 690±10℃×2h heat treatment is required after welding to eliminate the welding residual stress and avoid the generation of cracks.
- Results and analysis
We conducted an appearance inspection on the steel plate according to the welding evaluation standard for pressure bearing equipment, and found that there were no defects such as pores, slag inclusion and cracks on the surface. Then, we conducted 100% radiographic inspection and mechanical properties tests such as tensile, bending and impact. The test results are shown in the table.
| Item | Width/mm | Thickness/mm | CSA/mm² | Maximum load | Tensile strength |
| I1 | 20.30 | 39.72 | 806.3 | 507.12 | 625 Mpa |
| I2 | 20.28 | 39.78 | 806.7 | 482.83 | 600 Mpa |
| Sample No. | Bend type | Thickness/mm | Bend diameter | Bend angle | Results |
| C1 | Lateral bending | 10 | D=40 mm | 180° | Qualified |
| C2 | Lateral bending | 10 | D=40 mm | 180° | Qualified |
| C3 | Lateral bending | 10 | D=40 mm | 180° | Qualified |
| Sample No. | Sample size mm | Gap position | Test temperature | Impact absorbing energy/Akv |
| R1 | 10*10*55 | A387 GR22 side | 0℃ | 152 |
| R2 | 10*10*55 | A387 GR22 side | 0℃ | 176 |
| R3 | 10*10*55 | A387 GR22 side | 0℃ | 122 |
From the data above, it can be seen that the tensile, bending and impact tests are all qualified, indicating that our welding process plan is qualified, the dissimilar material steel plate welding between ASTM A387 Grade 22 and 304 are perfectly feasible.


